Homepage
| Organic waste
| Anaerobic
digestion
| Biogas
| Biogas installations
| Economy of biogas installations
Biogas incomes
| Sludge
| Projects Gallery | Contact
Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic Digestion Diagram
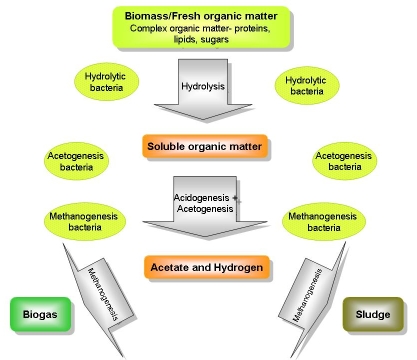
Hydrolysis
The organic macromolecules break up into simpler elements -
solid
waste thus is liquefied and hydrolyzed in small soluble molecules (e.g.
the cellulose is transformed into soluble sugars such as glucose or
cellobiose.
Acidogenesis
This process transforms these simple molecules into acids of weak molecular weight such as lactic acid and volatile fatty-acids from 2 to 5 carbon atoms. In parallel are produced low-weight molecular alcohol, such as bicarbonate ethanol and molecular hydrogen.
Acetogenesis
The products resulting from fermentation require an additional
transformation before being able to produce methane. It is here that
intervene the acetogenes reducing bacteria and the sulfato-reducing
bacteria, producing hydrogen sulphide (H2S)
Methanogenesis
The ultimate phase during which two types of methanogenes
bacteria
take over: the first ones (acetogenes) reduce methane acetate, CH4 and
bicarbonate. The second ones, reduce methane bicarbonate.